The escalating importance of robust incident management processes has led to the widespread adoption of standardized reporting tools. Among these, the Incident Report Register Template has emerged as a critical component for efficient record-keeping, analysis, and continuous improvement. This article will delve into the benefits of utilizing a well-designed Incident Report Register Template, exploring its key features, advantages, and practical implementation considerations. Incident Report Register Template is more than just a document; it’s a strategic asset for any organization seeking to proactively identify, analyze, and mitigate potential risks. It’s a foundational element for fostering a culture of safety and operational excellence.
The Need for a Standardized Incident Reporting System
Organizations today face an increasingly complex and dynamic operational environment. Traditional reactive incident response methods often struggle to keep pace with the sheer volume of incidents occurring across various departments and functions. A centralized, standardized approach to incident reporting is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity for maintaining operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, and ultimately, customer satisfaction. The lack of a consistent reporting system can lead to fragmented data, duplicated efforts, and a failure to learn from past incidents. A robust Incident Report Register Template provides a structured framework for capturing, analyzing, and disseminating incident information, enabling organizations to move beyond simply reacting to problems and proactively prevent them from recurring. The ability to quickly and accurately assess the impact of an incident is paramount for informed decision-making.
Key Features of a Comprehensive Incident Report Register Template
A truly effective Incident Report Register Template goes beyond simply collecting data. It incorporates features designed to facilitate thorough analysis and continuous improvement. Here’s a breakdown of essential elements:
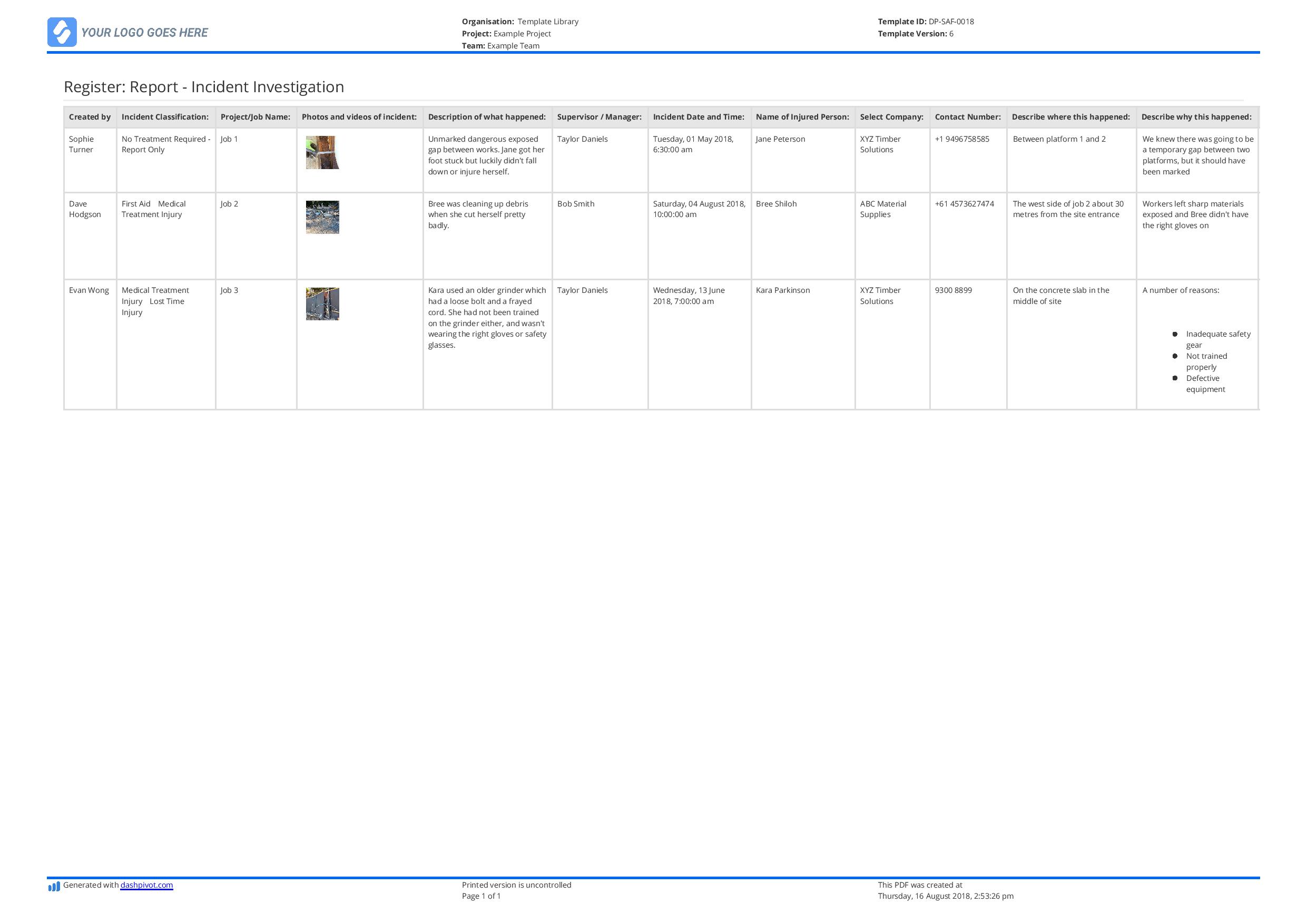
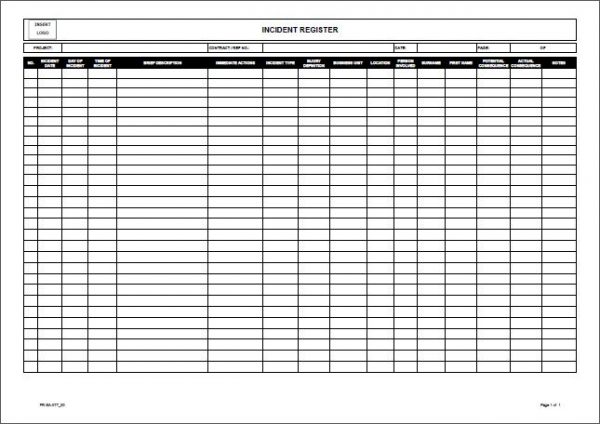
- Incident ID: A unique identifier for each incident, crucial for tracking and referencing.
- Date and Time of Incident: Precise timestamping is vital for chronological analysis.
- Reporting Party: Identifies the individual or team responsible for reporting the incident.
- Incident Type: Categorizes the incident based on its nature (e.g., system outage, security breach, human error).
- Severity Level: A standardized scale to assess the impact of the incident (e.g., Critical, High, Medium, Low).
- Impact Assessment: Details the consequences of the incident on operations, customers, and the organization as a whole.
- Root Cause Analysis: A section dedicated to identifying the underlying factors that contributed to the incident.
- Corrective Actions Taken: A record of steps taken to resolve the incident and prevent recurrence.
- Lessons Learned: A space for capturing insights gained from the incident, including recommendations for improvement.
- Supporting Documentation: Links to relevant logs, reports, and other data sources.
Advantages of Implementing an Incident Report Register Template
The benefits of adopting a well-designed Incident Report Register Template are numerous and far-reaching. Here’s a look at some key advantages:
- Improved Incident Management: Provides a clear and consistent view of incidents across the organization, streamlining the incident response process.
- Enhanced Data Analysis: Facilitates the collection and analysis of incident data, enabling identification of trends and patterns.
- Increased Operational Efficiency: Reduces the time and effort required to document and resolve incidents.
- Reduced Risk: Proactively identifies and mitigates potential risks by analyzing incident data.
- Regulatory Compliance: Supports compliance with industry regulations and standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
- Continuous Improvement: Provides a platform for continuous improvement through the implementation of lessons learned.
- Better Communication: Standardized reporting facilitates clear and consistent communication among stakeholders.
Structuring the Incident Report Register Template: A Practical Guide
A well-structured Incident Report Register Template is key to its effectiveness. Here’s a suggested layout:
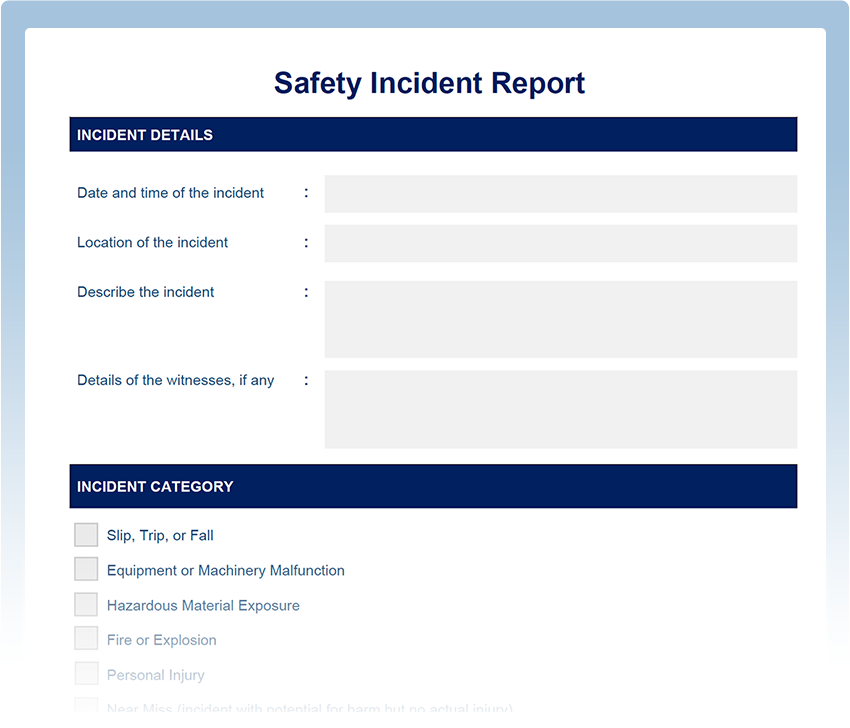
Section 1: Incident Overview
- Incident ID: [Unique Identifier]
- Date and Time of Incident: [Timestamp]
- Reporting Party: [Name and Department]
- Incident Type: [Categorization]
Section 2: Detailed Incident Description
- What Happened? A concise narrative of the incident.
- Sequence of Events: A chronological breakdown of the incident’s progression.
- Affected Systems/Processes: A list of impacted systems, applications, or workflows.
- User Impact: Quantify the impact on users (e.g., number of affected users, time lost).
Section 3: Root Cause Analysis
- Potential Causes: A list of potential contributing factors.
- Root Cause: The underlying reason for the incident.
- Contributing Factors: Further details about the factors that exacerbated the issue.
Section 4: Corrective Actions
- Implemented Solutions: A record of the actions taken to resolve the incident.
- Verification of Effectiveness: Confirmation that the corrective actions have successfully addressed the root cause.
- Post-Implementation Monitoring: Plans for ongoing monitoring to prevent recurrence.
Section 5: Lessons Learned
- Key Findings: Summarized insights from the incident.
- Recommendations: Specific, actionable recommendations for improvement.
- Action Items: Assigning responsibility and deadlines for implementing recommendations.
Section 6: Supporting Documentation
- Links to relevant logs, reports, and system configurations.
The Role of Technology in Incident Report Register Template Implementation
While a well-designed template is paramount, technology can significantly enhance its usability and effectiveness. Consider utilizing:
- Cloud-Based Reporting Platforms: These platforms offer robust features for data collection, analysis, and reporting.
- Workflow Automation: Automate the process of incident creation, assignment, and tracking.
- Data Visualization Tools: Create charts and graphs to visualize incident trends and patterns.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Connect the Incident Report Register Template to other relevant systems (e.g., ticketing systems, CMDB).
Conclusion: Investing in a Robust Incident Report Register Template
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, a proactive and well-documented incident management system is no longer optional – it’s a strategic imperative. The Incident Report Register Template provides a foundational framework for capturing, analyzing, and learning from incidents, ultimately contributing to improved operational efficiency, reduced risk, and enhanced customer satisfaction. By embracing a standardized approach to incident reporting, organizations can transform their incident response capabilities and achieve a sustainable culture of continuous improvement. Incident Report Register Template is an investment in the future of your organization’s resilience and success.