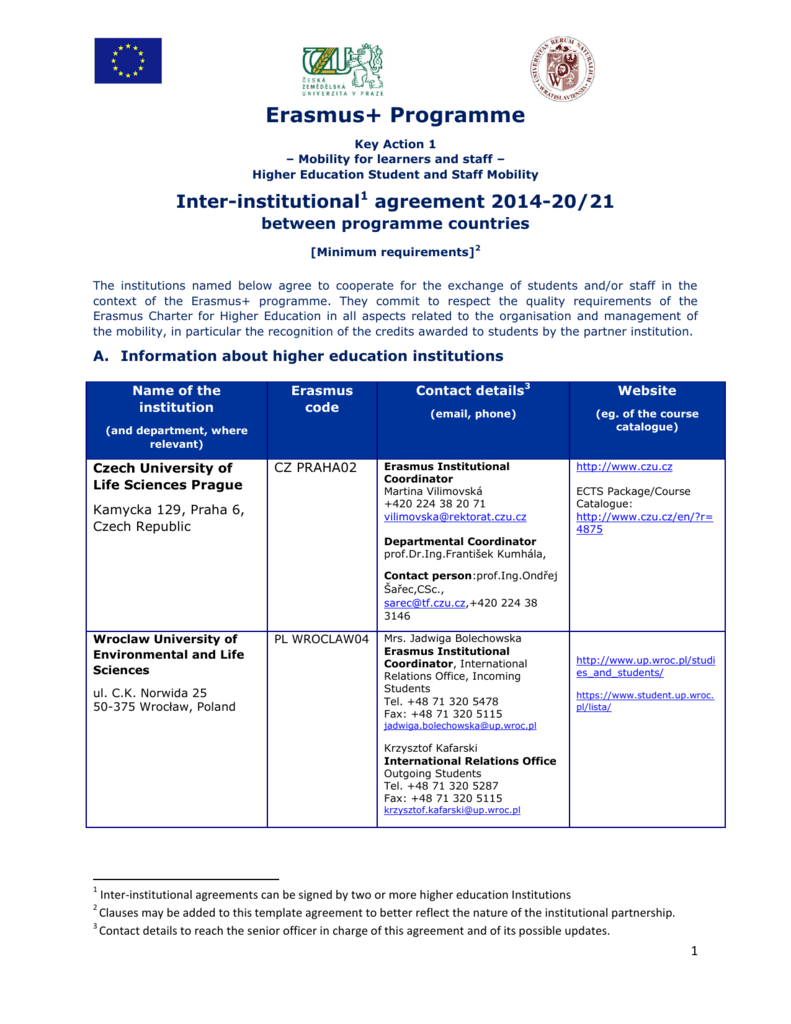
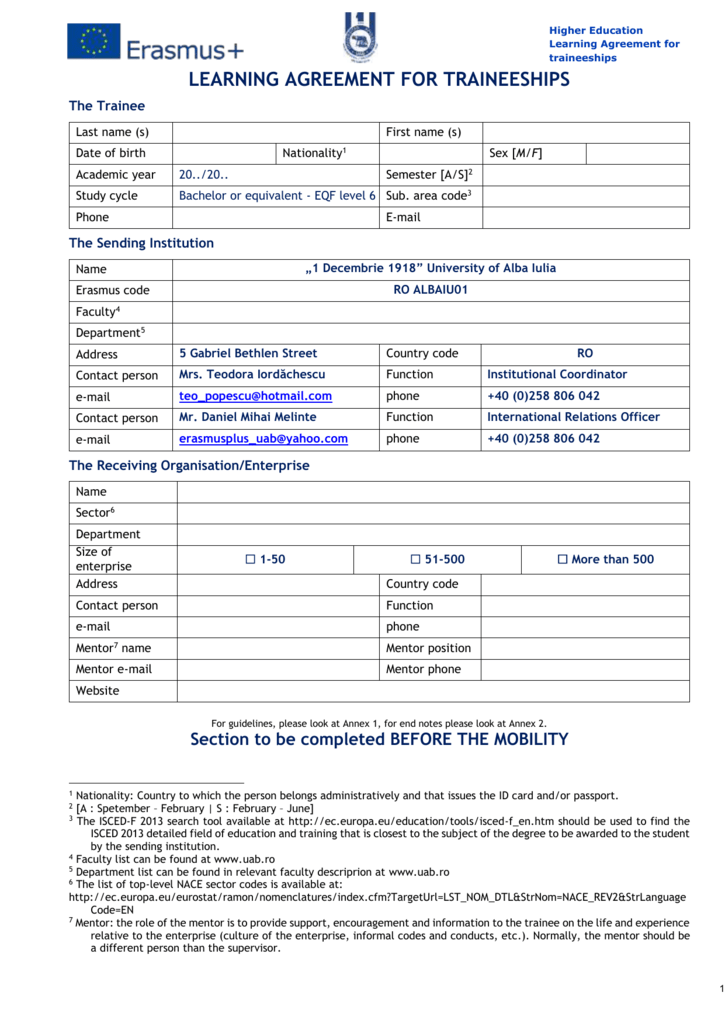
The Erasmus program, a cornerstone of European higher education, facilitates student exchange and mobility. Understanding the legal framework surrounding this program is crucial for both host and recipient institutions. A robust and well-drafted Erasmus Bilateral Agreement Template is the foundation for a successful and legally sound exchange. This article will delve into the essential components of such a template, providing a comprehensive guide for institutions seeking to establish and manage Erasmus agreements. The core of this agreement is a legally binding contract outlining the terms and conditions of the exchange, ensuring clarity and minimizing potential disputes. It’s vital to consult with legal counsel specializing in international education law to ensure compliance with all applicable regulations. The template itself is a starting point; tailoring it to specific institutional needs and the nature of the exchange is paramount. This guide will cover the key sections and considerations involved in creating a comprehensive Erasmus Bilateral Agreement Template.
Understanding the Importance of a Template
Before diving into the specifics, it’s important to recognize why a well-structured template is so critical. A template provides a standardized framework, reducing the risk of misunderstandings and potential legal challenges. It clearly defines responsibilities, liabilities, and dispute resolution mechanisms. Furthermore, it streamlines the process of onboarding new exchange partners, ensuring a smooth and efficient start to the program. Without a template, institutions risk significant delays, increased administrative burdens, and potential legal complications. The template acts as a roadmap, guiding all parties through the complexities of the exchange.
Key Sections of an Erasmus Bilateral Agreement Template
Let’s examine the essential sections typically included in an Erasmus Bilateral Agreement Template. Each section requires careful consideration and precise wording to ensure its effectiveness.
1. Introduction and Parties Involved
The initial section establishes the purpose and scope of the agreement. It clearly identifies the participating institutions – the host institution and the recipient institution. It also outlines the parties involved – the institution responsible for managing the exchange and the institution being exchanged. This section is crucial for establishing a clear understanding of who is responsible for what. It’s important to include contact information for all parties involved, facilitating communication and coordination. A concise statement about the program’s objectives and the expected outcomes is also beneficial. For example, “This agreement outlines the terms and conditions for the exchange program between [Host Institution Name] and [Recipient Institution Name], designed to promote student mobility and enhance international collaboration.”
2. Exchange Objectives and Scope
This section details the specific goals of the exchange program. What are the intended outcomes? Are there specific areas of focus, such as research collaboration, cultural exchange, or professional development? Defining clear objectives helps to ensure that the exchange is aligned with the institution’s strategic goals. It’s important to specify the duration of the exchange, including start and end dates. Furthermore, the scope of the exchange – which subjects, disciplines, and locations are covered – should be clearly defined. For instance, “This agreement covers a 12-month exchange program between [Host Institution Name] and [Recipient Institution Name], focusing on [Specific Subject Area] and taking place in [Specific Location].”
3. Student Responsibilities
This section outlines the obligations of the host institution and the recipient institution. It’s vital to clearly define the responsibilities of each party, including ensuring student visa compliance, providing accommodation, and facilitating access to resources. It’s crucial to specify the procedures for student registration, visa applications, and accommodation arrangements. The agreement should address issues such as student health insurance, academic support, and cultural orientation. For example, “The host institution is responsible for ensuring that all students enrolled in this exchange program meet all visa requirements and receive appropriate health insurance coverage. The recipient institution is responsible for providing a suitable accommodation and facilitating access to academic support services.”
4. Academic Responsibilities
This section addresses the academic aspects of the exchange. It specifies the requirements for student enrollment, course selection, and academic assessment. It should outline the procedures for academic advising, mentorship, and the evaluation of student performance. It’s important to clarify the process for academic record transfer and the rules regarding academic credit earned during the exchange. For example, “Students participating in this exchange program are required to maintain a minimum GPA of [GPA] and to submit their academic records to the host institution prior to the start of the exchange. The recipient institution will review these records and provide feedback to the student.”
5. Financial Responsibilities
This section covers the financial aspects of the exchange. It details the costs associated with the program, including tuition fees, accommodation, travel expenses, and living expenses. It should specify the reimbursement policies for expenses incurred during the exchange. It’s important to clearly outline the procedures for managing student funds and ensuring compliance with financial regulations. For example, “The host institution will reimburse students for reasonable travel expenses incurred during the exchange program, subject to a maximum reimbursement of [Amount]. Students are responsible for covering their own accommodation and living expenses.”
6. Cultural Responsibilities
Recognizing the importance of cultural exchange, this section addresses the responsibilities of both parties in fostering an inclusive and respectful environment. It emphasizes the importance of promoting intercultural understanding and respect. It may include provisions for cultural orientation activities and the facilitation of student interaction with local communities. For example, “Both parties are committed to promoting a welcoming and inclusive environment for all students participating in this exchange program. The host institution will provide cultural orientation activities to help students familiarize themselves with the local culture, and the recipient institution will facilitate opportunities for student interaction with local communities.”
7. Dispute Resolution
This section outlines the process for resolving any disputes that may arise during the exchange. It specifies the procedures for mediation, arbitration, or litigation. It’s crucial to establish clear timelines for resolving disputes and to ensure that all parties have the opportunity to participate in the dispute resolution process. For example, “In the event of a dispute arising during the exchange program, the parties will first attempt to resolve the issue through mediation. If mediation is unsuccessful, the parties will submit the dispute to arbitration. The arbitration will be conducted by a neutral third party.”
8. Termination and Exit Procedures
This section clarifies the conditions under which the exchange program can be terminated, and the procedures for withdrawing students. It should outline the responsibilities of both parties in ensuring a smooth exit process. For example, “The host institution may terminate the exchange program with [Number] days’ notice if the student does not meet the academic requirements. The recipient institution will provide the student with a refund of any tuition fees paid.”
9. Governing Law and Jurisdiction
This section specifies the governing law for the agreement and the jurisdiction for resolving any disputes. It’s important to clearly define which country’s laws will apply to the agreement. For example, “This agreement shall be governed by the laws of [Country Name]. Any disputes arising under this agreement shall be resolved by the courts of [Country Name].”
Conclusion
The Erasmus Bilateral Agreement Template is a vital tool for facilitating successful and sustainable exchange programs. By carefully considering each section and tailoring the template to the specific needs of the participating institutions, both host and recipient can ensure a legally sound and mutually beneficial partnership. Remember that ongoing communication, clear expectations, and a commitment to mutual respect are essential for the long-term success of the exchange. Regular review and updates to the template are also recommended to reflect evolving regulations and best practices. Investing in a well-crafted template demonstrates a commitment to quality and enhances the overall experience for all involved. Ultimately, a robust template is a cornerstone of a successful Erasmus program, fostering collaboration and enriching the lives of students and institutions alike.