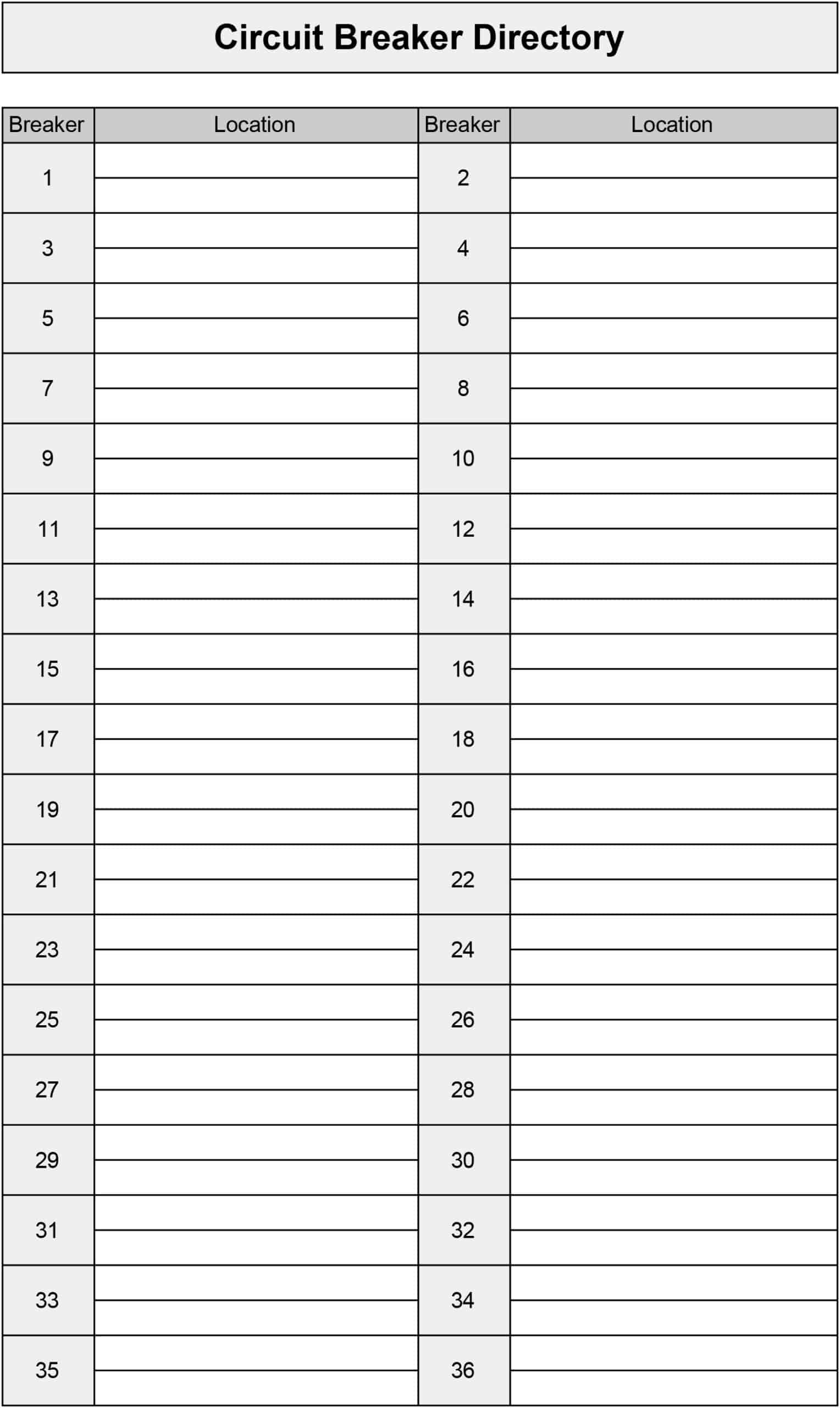
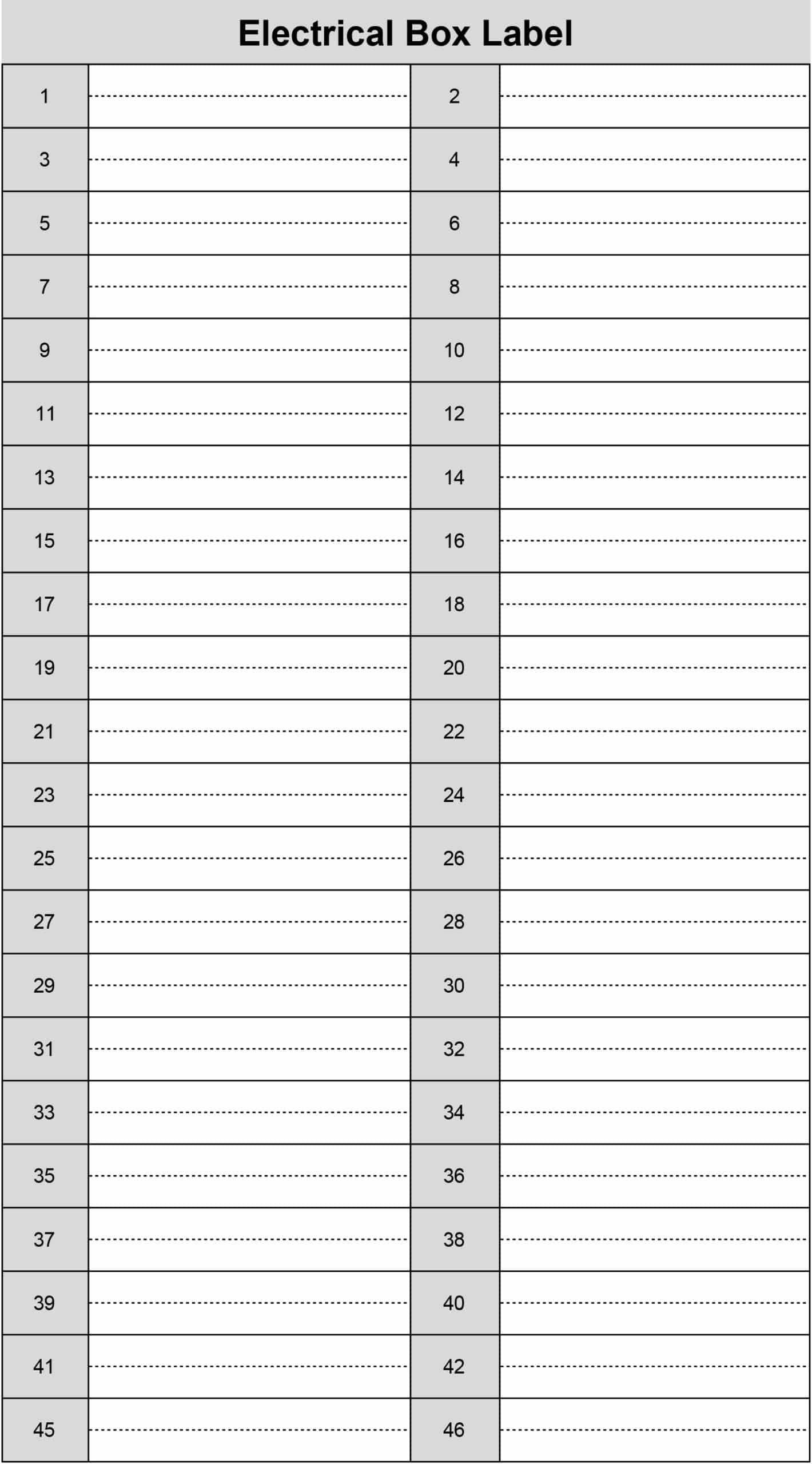
Designing a clear and consistent system for labeling circuit breaker panels is crucial for efficient troubleshooting, maintenance, and regulatory compliance. A well-structured labeling system minimizes confusion, reduces errors, and streamlines the entire process. This article will delve into the essential elements of creating a robust and effective Circuit Breaker Panel Labels Template, providing you with the knowledge and resources to implement a solution tailored to your specific needs. The core of this process revolves around accurately representing the function and configuration of each breaker, ensuring that technicians can quickly and confidently identify and resolve issues. Understanding the principles behind effective labeling is paramount for maintaining a safe and reliable electrical system. This template offers a comprehensive guide, covering everything from design considerations to practical implementation. Let’s explore how to build a system that truly works.
Understanding the Importance of Labeling
The initial investment in a well-designed labeling system is a significant one, but the long-term benefits far outweigh the costs. Poorly labeled panels can lead to wasted time, increased labor costs, and potentially dangerous situations. Accurate labeling minimizes the risk of incorrect breaker selection, preventing damage to equipment and ensuring compliance with safety regulations. Furthermore, a standardized system promotes consistency across different teams and locations, fostering teamwork and improving overall operational efficiency. Without a clear and consistent approach, troubleshooting becomes a frustrating and time-consuming process, hindering productivity and potentially compromising safety. The benefits extend beyond simple troubleshooting; a thoughtfully designed labeling system also supports regulatory compliance, demonstrating a commitment to safety and responsible electrical practices. Proper labeling is not just a matter of aesthetics; it’s a fundamental element of a well-managed electrical system.
Key Components of a Circuit Breaker Panel Labels Template
A successful Circuit Breaker Panel Labels Template isn’t simply a list of numbers. It’s a carefully constructed system that incorporates several key elements. The template should be easily adaptable to different breaker types and configurations. Consider these essential components:
- Breaker Type: Clearly identify the type of breaker (e.g., Tripped, Burstered, Thermal, Ground Fault).
- Circuit Number: Assign a unique number to each breaker.
- Circuit Description: Provide a concise description of the circuit’s function (e.g., “Residential Main,” “Industrial Power,” “Data Network”).
- Voltage: Indicate the voltage level of the circuit (e.g., 120V, 240V).
- Load: Specify the type of load connected to the circuit (e.g., Lighting, Appliances, HVAC).
- Protection Type: Describe the type of protection the breaker provides (e.g., Overcurrent, Short Circuit, Ground Fault).
- Notes/Comments: A space for additional information, such as specific settings or maintenance requirements.
Section 1: Breaker Type – A Fundamental Foundation
This section is the cornerstone of any effective labeling system. It establishes a consistent framework for identifying and categorizing different breaker types. A robust system will include a clear and concise table or list, detailing the characteristics of each breaker type. Consider including a brief explanation of each breaker type’s primary function to enhance understanding. For example, a “Tripped” breaker might be labeled as “Primary Circuit Control,” while a “Thermal” breaker could be described as “Overheat Protection.” Maintaining a consistent terminology across all breaker types is critical for accurate identification. This section should be easily accessible and readily understood by all technicians.
Section 2: Circuit Number – Ensuring Uniqueness
Assigning unique circuit numbers is essential for tracking and managing breaker installations. Each breaker should have a distinct number, preventing confusion and ensuring that breakers are properly identified and located. The numbering system should be standardized and consistently applied across all panels. Consider using a sequential numbering system (e.g., 1, 2, 3…) or a system that incorporates a unique identifier (e.g., a serial number). Clearly document the numbering system used and ensure that all technicians are trained on its application. A well-defined numbering system simplifies troubleshooting and reduces the risk of errors.
Section 3: Circuit Description – Providing Context
The circuit description provides a brief overview of the circuit’s purpose, aiding technicians in quickly understanding the function of the breaker. This section should be concise and informative, avoiding technical jargon. For example, “Residential Main” describes a circuit supplying power to a typical residential dwelling. “Industrial Power” indicates a circuit supplying power to industrial equipment. Providing context helps technicians quickly grasp the scope of the circuit’s operation. This section should be easily adaptable to different circuit types and applications.
Section 4: Voltage – Critical for Safety
Voltage is a fundamental parameter that must be clearly indicated. The voltage level of the circuit should be explicitly stated, ensuring that technicians are aware of the potential hazards associated with the circuit. This information is crucial for preventing electrical shock and ensuring compliance with safety regulations. Clearly label the voltage level (e.g., 120V, 240V) and provide a brief explanation of its significance. Consider including a warning about potential hazards associated with incorrect voltage levels.
Section 5: Load – Understanding the Circuit’s Function
The load type associated with the circuit is equally important. This information helps technicians understand the type of equipment or devices that are connected to the circuit. For example, a “Lighting” circuit might be connected to fluorescent lights, while an “HVAC” circuit might be connected to a heating and cooling system. Clearly define the load type and provide a brief explanation of its function. This information is essential for determining the appropriate breaker settings and ensuring the safe operation of the circuit.
Section 6: Protection Type – Identifying the Safety Features
The protection type assigned to the breaker describes the type of safety feature that is provided. Common protection types include Overcurrent, Short Circuit, and Ground Fault. Understanding the protection type is crucial for assessing the safety of the circuit and identifying potential hazards. For example, an “Overcurrent” breaker protects against excessive current flow, while a “Short Circuit” breaker protects against accidental connection of conductors. Clearly define the protection type and provide a brief explanation of its function.
Section 7: Notes/Comments – For Additional Information
This section provides a space for technicians to add any additional information that may be relevant to the circuit. This could include specific settings, maintenance requirements, or any other pertinent details. It’s a valuable tool for providing context and ensuring that all technicians have access to the same information. This section should be easily accessible and readily understood by all technicians.
Section 8: Standardized Labeling Conventions – Consistency is Key
To ensure consistency and accuracy, it’s essential to establish a standardized labeling convention. This involves defining a consistent format for all labels, including the use of standardized symbols, abbreviations, and terminology. Consider using a template or a spreadsheet to ensure that all labels are created consistently. Regularly review and update the labeling convention to reflect changes in regulations or industry best practices. A well-defined standard will minimize errors and improve the overall efficiency of the labeling process.
Conclusion
Creating a robust and effective Circuit Breaker Panel Labels Template is a critical investment for any organization operating in the electrical industry. By carefully considering the key components outlined in this article, and by adhering to a standardized labeling convention, you can significantly improve the efficiency, accuracy, and safety of your electrical system. The benefits of a well-designed labeling system – reduced troubleshooting time, minimized errors, and enhanced regulatory compliance – far outweigh the initial investment. Remember that a consistent and well-maintained labeling system is an ongoing process, requiring regular review and updates to ensure its continued effectiveness. Investing in a quality labeling system is an investment in the safety and reliability of your electrical infrastructure.